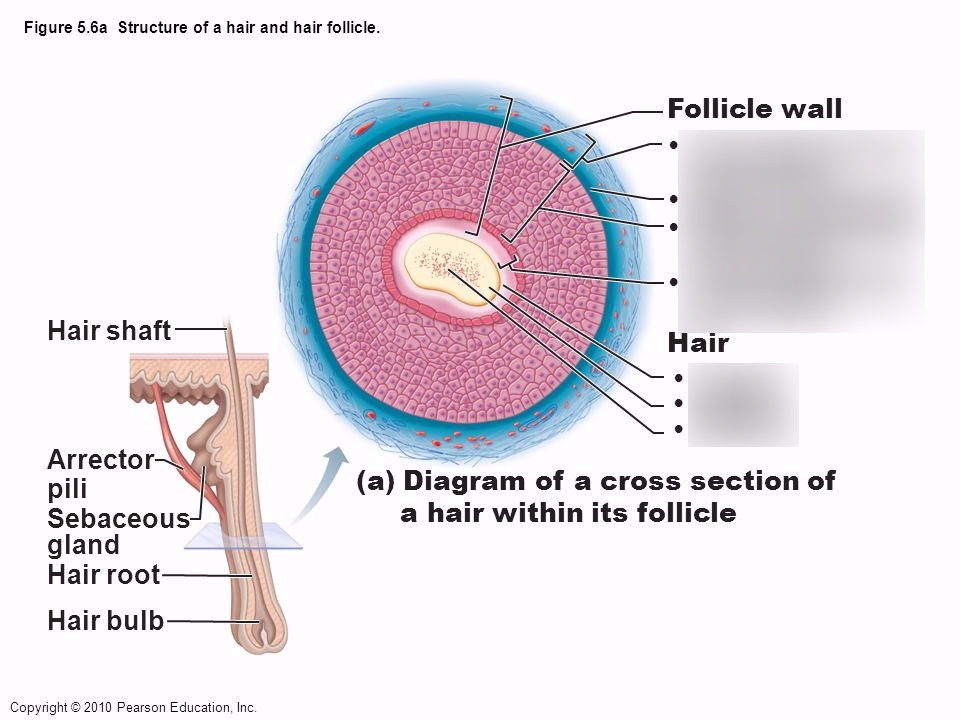
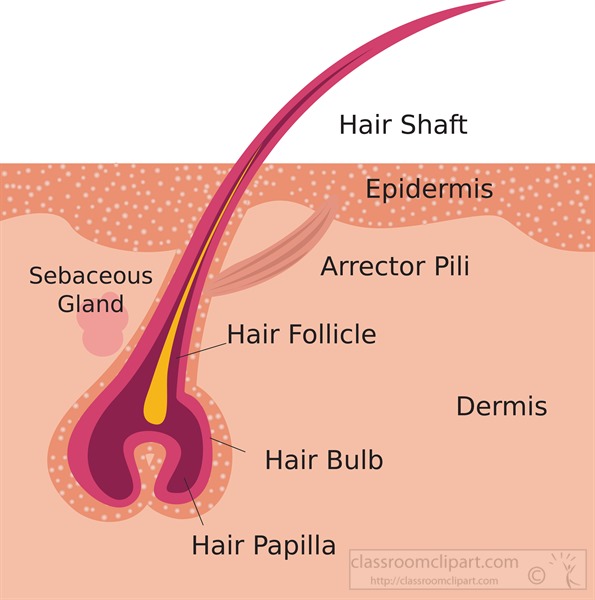
Hair follicle: anatomy and function
Table Of Content
Melatonin promotes hair follicle growth in humans and secondary hair follicle growth in goats. Melatonin promotes human and goat oocyte competence under in vitro culture conditions. Figure 1 PRISMA diagram of the process of study selection and traditional meta-analysis. We followed the steps to screen the retrieved literature and ended up with 22 articles.
Alopecia Areata
In wool fibres as well as human hair, the cortical cells were observed to be divided into different regions termed orthocortex, paracortex and mesocortex (Mercer, 1953). The difference in distribution of these cell types is an important factor for determining the curvature of the hair fibre (Kajiura et al., 2006). In particular, straight hair tends to have symmetrical distribution of the ortho- and paracortices whereas curly hair tends to have a non-symmetrical distribution of these cortical cells (Kajiura et al., 2006). Most of the cortical cells are composed of a protein known as keratin (Robbins, 2012). The purpose of this study is to use X-ray diffraction to analyze the structure of human scalp hair for individuals with differing characteristics. The 12 individuals in this study include hair from men and women and hair of different colour and appearance, such as straight, wavy and curly.
Study selection and characteristics
A number of hair conditions are caused by issues with hair follicles. If you think you have a hair condition, or if you have unexplained symptoms like hair loss, it’s best to consult with a dermatologist. Hair follicles aren’t just responsible for how much your hair grows, they also influence what your hair looks like. The shape of your follicle determines how curly your hair is. Circular follicles produce straight hair while oval follicles produce curlier hair.
Microanatomy of Catagen Phase Hair
However, there was a positive correlation with secondary follicle growth. Whether it is straight or curly will depend on the cross-sectional shape of hair. The more oval-shaped the cross-section is, the curlier the hair will be. At the base of the hair, the hair root widens to a round hair bulb.
Scars Mended Using Transplanted Hair Follicles - Neuroscience News
Scars Mended Using Transplanted Hair Follicles.
Posted: Fri, 06 Jan 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
Furthermore, you can cut your hair or shave without damaging the hair structure because the cut is superficial. Most chemical hair removers also act superficially; however, electrolysis and yanking both attempt to destroy the hair bulb so hair cannot grow. We studied the molecular hair structure of several individuals using X-ray diffraction. Hair samples were collected from 12 healthy individuals of various characteristics, such as gender, optical appearance and genetic relation. Signals corresponding to the coiled-coil phase of the keratin molecules, the formation of intermediate filaments in the cortex and from the lipid molecules in the cell membrane complex were observed in the experiment.
What color are hair follicles?
In the precortical matrix, these melanosomes are transferred to the hair shaft keratinocytes and formed a pigmented hair shaft. The hair follicle also contains melanocyte stem cells, which are located in the bulge and in the secondary hair [33–35]. In the second stage of development, hair germ elongates into a cord of epithelial cells and forms the hair peg (stages 3 and 4). It is surrounded by mesenchymal cells that eventually transformed to the fibrous sheath. Derived from the epithelial cells of the hair peg, hair matrix cells form the hair shaft and inner root sheath (IRS). Outer root sheath (ORS) generates two bulges along the side of the hair follicle, the proximal bulge serves as a reservoir for epithelial stem cells and the distal bulge evolves to sebaceous glands.
3. Molecular structure
The color of the hair is determined by the amount of melanin in the hardened cells. This can vary a lot from person to person, and it changes over the course of a lifetime. The amount of melanin typically decreases as people get older, and more air gets trapped inside the hair – it then loses its color and turns white.
Hair Follicle Functions
As you get older, your hair can change color, texture, and thickness. It can even change some of its location, with too much in some areas and too little in others. Our experts continually monitor the health and wellness space, and we update our articles when new information becomes available. Telogen effluvium is usually temporary and doesn’t require treatment.
The data in (C) (individuals 9 and 12) are from identical twins. Data in (D) was taken from fraternal twins (individuals 10 and 11). While different individuals in general show different membrane patterns (A), features in (B) and (C) perfectly agree. Fraternal twins show slight differences in their pattern in (D). In the direction perpendicular to the hair fibre axis (q‖), there are also two major peaks consistent among all subjects, one narrow peak around 9.5 Å and one broad peak around 4.3 Å. The total scattering profile was well fit by two Lorentzian peak profiles (and a background), whose positions is plotted in Fig.
Primary hair follicles are generally considered the hair that has already developed. The results of the present study showed that there was no correlation between melatonin and goat primary follicle density. However, melatonin was positively correlated with goat secondary follicle density.
These signals are related to the coiled-coils arrangement of the keratin proteins in the cortex, the formation of intermediate filaments in the cortex, and lipids in the cell membrane complex of the hair. Statistical analysis of the corresponding molecular dimensions revealed a rather small distribution between different individuals. These general properties of human hair are observed in all hair independent of gender, colour or optical appearance of the hair (as listed in Table 1) within the number of individuals included in this study.
In this stage, the dermal papilla moves upward, following the epithelial sac. The middle layer of the hair shaft (hair cortex) constitutes the bulk of the hair and consists of cells that keratinize gradually as they move upward from the hair matrix. Unlike the IRS, which keratinizes by forming trichohyalin granules (soft keratin), the hair cortex cells keratinize without forming granules (the aforementioned trichilemmal keratinization). However, they keratinize relatively low in the hair follicle and are indistinguishable at higher levels, where they function as a single unit covering the hair shaft. The IRS stains deeply with toluidine blue because of the presence of the amino acid citrulline. The macro-environment surrounding the hair follicle also takes part in regulating cycle transitions.
Hair shaft synthesis and pigmentation only take place in anagen [11]. The degree of axial symmetry within the hair bulb determines the curvature of the final hair structure [35]. Fiber length is often dependent on the duration of the anagen or actively growing phase of the follicle [17]. The featured regulatory proteins in anagen phase are BMPs, sonic hedgehog, several WNT proteins and receptors. Insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), fibroblast growth factor-7 hepatic growth factor (HGF), and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are thought to be important for anagen maintenance [36]. Lanugo, vellus and terminal hairs follow the same basic architectural principles.
Comments
Post a Comment